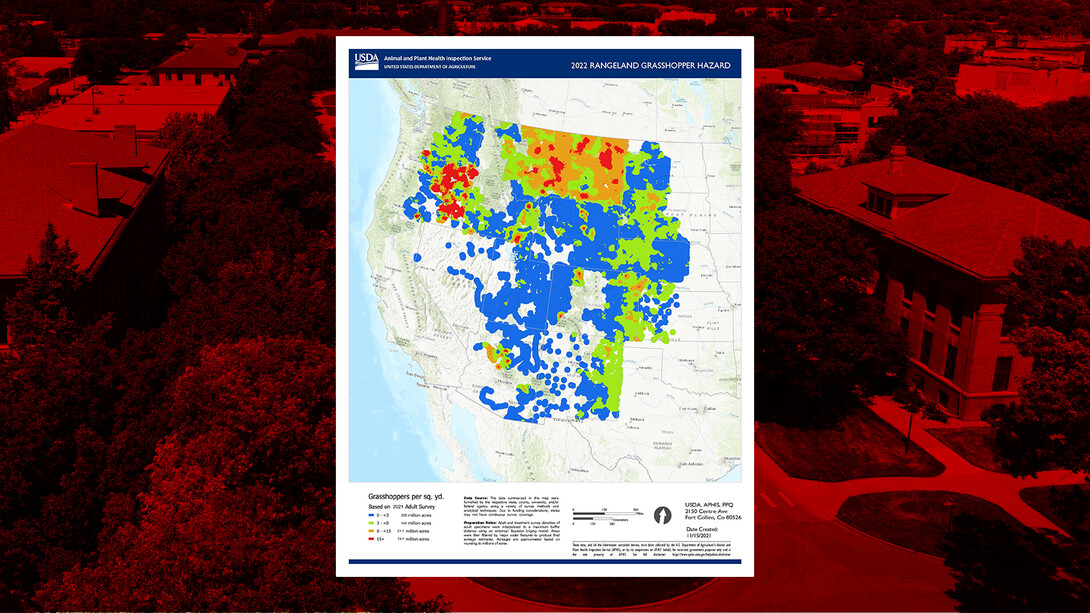
Lincoln, Neb. —The risk of grasshopper infestation in Nebraska rangelands will be low in 2022, with a slightly higher risk in southwestern Nebraska, based on fall adult surveys conducted by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (USDA-APHIS).
As the accompanying map illustrates, a majority of the western United States is projected to have very low numbers. USDA-APHIS continues to provide us with regular updates on the status of rangeland grasshoppers across Nebraska.
Grasshopper numbers are responsive to environmental conditions; however, species differ in their response to precipitation, plant communities, soil characteristics, and microclimate. A wet spring and rains at time of grasshopper hatching and development (mid-May-June) improves rangeland forage quality and reduces the loss from grasshopper infestation.
Current long-range weather forecasts through March have indicated normal conditions, which might mean a continuation of cool, dry weather through the end of March. However, conditions beyond March appear to have a high degree of uncertainly at present.
Spotty occurrences of high grasshopper densities often occur throughout western Nebraska even in low-risk years. Therefore, ranchers and range managers should maintain vigilance to monitor grasshopper densities during hatching periods.
Keep an eye on Nebraska Extension’s CropWatch website (https://cropwatch.unl.edu) later this season for information on how to scout for rangeland grasshoppers.







